Aerodyne Aerosol Time of Flight Mass Spectrometer (TOF-AMS)
The Aerodyne Aerosol Time of Flight Mass Spectrometer (TOF-AMS) is an instrument manufactured by Aerodyne Research Inc. and is used to study the chemical and physical nature of aerosol particles online. The instrument works by focusing the sampled particles into a tightly collimated beam at its inlet and skimming off the majority of the gas phase material before impacting them onto a heated tungsten surface. The non-refractory components of the particles instantly vaporise and the vapours produced are analysed using electron ionisation mass spectrometry. The particle beam can also be modulated using a chopper wheel and the particle sizes calculated by measuring their velocities.
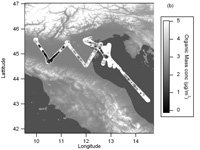
Scientifically, the instrument can deliver quantitative mass concentrations of the major non-refractory chemical species present in submicron particles (ammonium, nitrate, sulphate, organics and non-sea-salt chloride) in microgrammes per cubic metre. It is also capable of delivering these concentrations as a function of diameter as a dM/dlog(D) distribution. Further to this, information on the chemical nature of the organic fraction can be derived by inspecting the relative sizes of the peaks within the mass spectrum. In order to produce fully quality assured and meaningful results, the data must be processed offline or near-real-time. Software tools to do this have been developed by the group at Manchester with our collaborators at Aerodyne and the University of Colorado at Boulder and use Igor Pro by Wavemetrics Inc. as a platform.
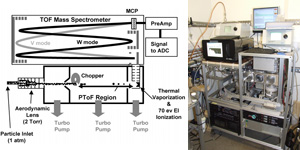
Fig1. Schematic of the H-TOF instrument (DeCarlo et al., 2006).
Fig2. The C-TOF deployed at Holme Moss in November 2006.
The SEAES Centre for Atmospheric Science has a long track record in AMS usage, both with the original quadrupole instruments (Q-AMS) and the newer TOF versions. We were the first institute outside of Aerodyne to take delivery of a production-model AMS back in 2000 and since then we have applied the instrument to a vast variety of applications in many different projects. In the field, they have been used at fixed surface sites, aircraft and ships and have also formed part of experiments in various laboratories, which include chamber work. Currently, we have three instruments; 2 x C-TOF-AMS and an H-TOF-AMS.
The Q-TOF is so-called because it used a Pfeiffer quadrupole mass spectrometer. Since its initial deployment on the FAAM aircraft in 2004, it was a mainstay of aerosol composition work on this platform. Notable campaigns included ITOP, ADRIEX, AMPEP, CLOPAP and AMMA. This instrument was upgraded to a C-TOF in October 2007 (see below). We also previously used a separate Q-AMS for mainly ground-based work between 2000 and 2006, but this has been upgraded to an H-TOF.
The time-of-flight (TOF) is a new variant on the AMS that replaces the traditional quadrupole mass spectrometer with an orthogonal extraction TOF mass spectrometer, produced by Tofwerk in Switzerland. This is a relatively new design, compatible with continuous ion sources such as the 70 eV electrons used by the AMS. There are two types of analyser used with the AMS; the compact and high resolution versions (C-TOF and H-TOF). The former is designed around a small package that is optimised for high sensitivity while the latter can be used for high-resolution applications such as elemental analysis. The immediate improvement over the quadrupole is one of vastly increased sensitivity, which in turn improves detection limits, signal-to-noise ratio of data and time resolution. Beyond this, the instrument is also capable of size-resolving the entire mass spectrum and deriving addition chemical information from the high-resolution spectra. We currently operate a C-TOF and an H-TOF for ground-based and laboratory measurements and a C-TOF on the FAAM aircraft.
References
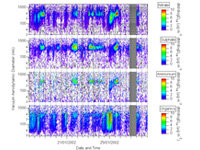
Size-resolved data measured in Manchester (updated version of Allan et al., J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos., 108, 4091, 2003).
Jayne et al. (2000), Development of an aerosol mass spectrometer for size and composition analysis of submicron particles, Aerosol Sci. Technol., 33, 49-70.
Allan et al. (2003), Quantitative sampling using an Aerodyne aerosol mass spectrometer - 1. Techniques of data interpretation and error analysis, J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos., 108, 4090.
Drewnick et al. (2005), A New Time-of-Flight Aerosol Mass Spectrometer (TOF-AMS)-Instrument Description and First Field Deployment, Aerosol Sci. Technol., 39, 637-658.
DeCarlo et al. (2006), Field-deployable, high-resolution, time-of-flight aerosol mass spectrometer, Anal. Chem., 78, 8281-8289.
Coe and Allan (2006), Mass Spectrometric Methods for Aerosol Composition Measurements, in Analytical Techniques for Atmospheric Measurement, edited by D. E. Heard, pp. 265-310, Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Canagaratna et al. (2007), Chemical and microphysical characterization of ambient aerosols with the Aerodyne aerosol mass spectrometer, Mass Spectrom. Rev., 26, 185-222.
External links
Tofwerk Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry
Support
The AMS instruments are partially supported by the NCAS Facility for Ground-based Atmospheric Measurement (FGAM) and NCAS Composition.
